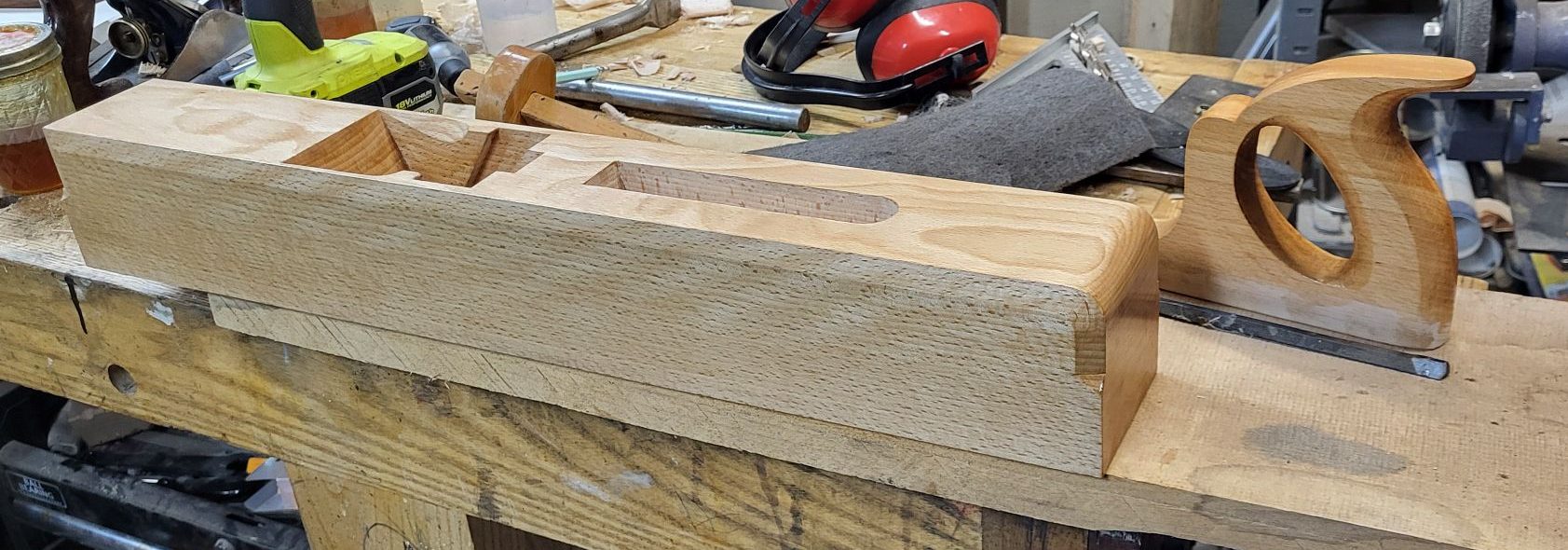
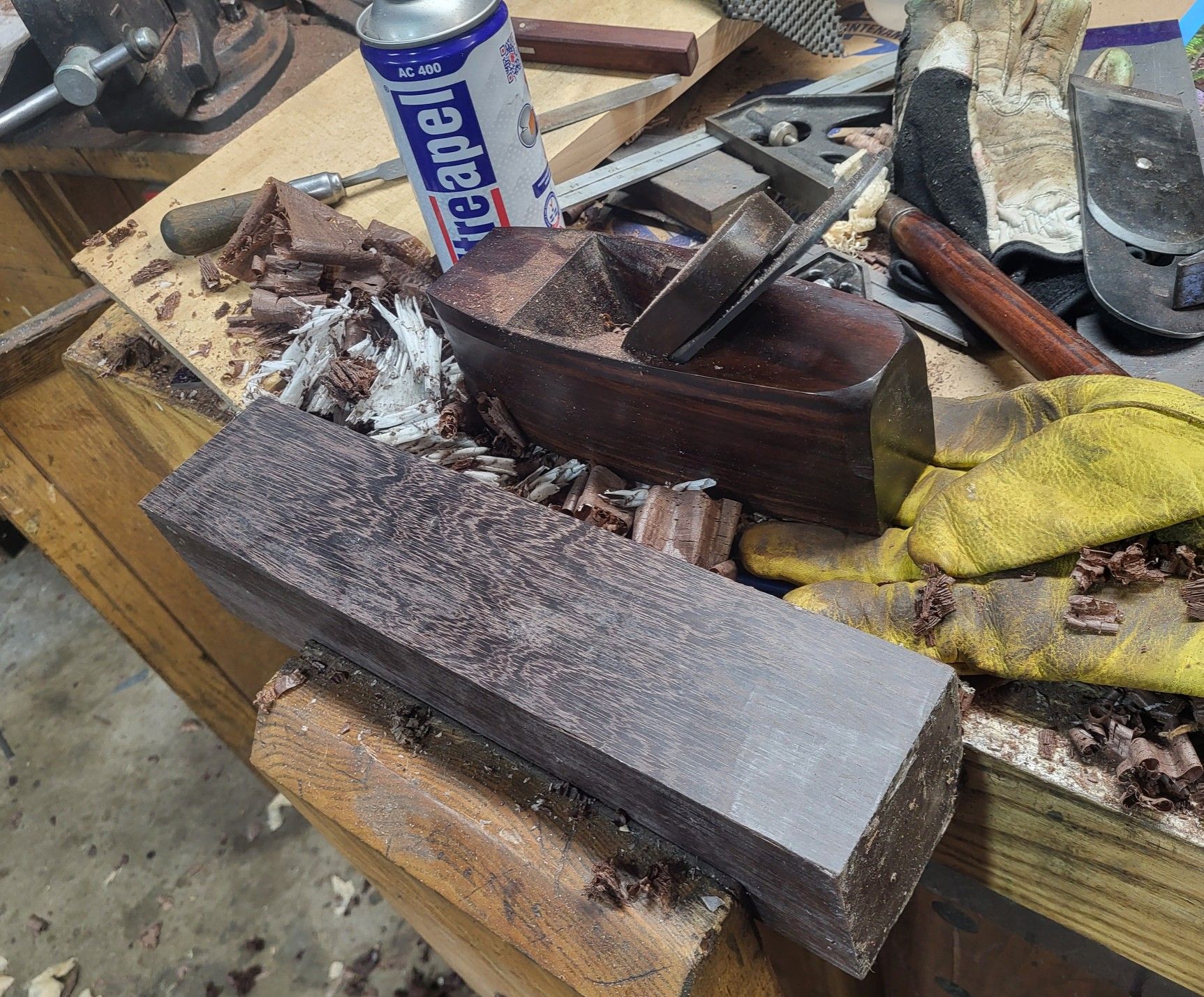
Not the last plane remaining to include shop made irons, but added to the closed handle rosewood jack, and the rosewood and gombeira smoothers.
Probably mentioned in another post, but I have two try planes of my own make. One was my first try plane, which was the third double iron bench plane I made. It’s OK. The second is a plane that I got lazy on and didn’t cut the mortise quite straight up and down. that one is actually solvable by adjusting the iron and cap iron, but I never did it. I use the first along with a vintage try plane that I like because sometimes I just like to use old stuff. There’s a credibility to the nice old stuff that my wares don’t have because……you can’t buy age, and you can’t buy provenance of a golden era plane that was made and sold in a competitive market of professional users. That’s gone.
What you can do us buy that older plane for less than the cost of materials in mine, so…there’s that.
This plane is euro beech, but the handle is american beech. It’s nicer than my earliest planes, and it has a 65 hardness plain steel iron in it. Those two together are important to me. Strength from hardness imparts edge stability. Plain steel at 65 means hardenable. The fact that it’s a 1.25% carbon steel means it’s still relatively relaxed getting to that hardness at a 400F temper or a few degrees above that.
There are still some things that could be improved in terms of lines. I chicken out on the handle and always leave the top and front strap a little tubbier than they need to be. A shorter handle looks nicer, too, but what if I decide to give the plane away? My hands across the knuckle are only about 3 1/2″ or a little wider. Someone with a 4″ hand across the knuckle could use this plane, but probably struggle on an older Mathieson plane until they realized they don’t need to have all four fingers on the handle.
Haven’t tested it yet, but anticipate no issues. This one is a little more free in the wear, etc, in terms of clearance in hopes that I won’t end up doing any extra work rubbing the shaving hard into the wear in tight quarters. Some of my tighter smoothers and jack planes do give a sense that the angle off of the cap iron into the wear, along with tightness, are so much so that even shavings not straightened by the cap are being straightened by the wear. It looks nice to have a plane that’s really tight like that, but there are limits to practicality.
I may build more planes this year, not sure – but in the background is a desire to make the chamfer a round over on the top, but elegant, change the carved details and make a much more artistic handle that’s not guarded by material bulk.
This is my first euro beech plane. At horizon, euro beech is still what’s available, and realistically, at not less than about $20 a board foot. Is that really a big deal? I guess it isn’t – if the wood is perfect, I’ll pay it. Some of the blanks on the page look less attractive. This one came out of a billet that wasn’t sawn that well, but there was room to resaw it, and the result is very attractive to my eye but for the contrast in how much color changes vs. american (oh, the wedge, too – also american to my recollection). I like the warmer color of the american stuff, but as this plane gets a few more coats of varnish, it will be sort of tarty and it has the wonderful three dimensional effect in that parts that are dark turn light and the converse as you’re walking past it, making it look a little alive.
If you look closely at the right eye in the last picture and the plane itself, you can tell that I corrected the bottom of the eye a little. It just looks better if the bottom of the eye doesn’t look like it flatten out entirely in the longer thin area of the eye.
There is a cap iron under the wedge, of course. You can’t see it and neither can I, but it’s there. Shop made like the rest of it, but for the modified knurled screw that I cannibalized to come up with the screw itself.
Oh, and the little bit of dirt trapped under the varnish on the front side of the handle – jeez. That stuff shows up less on the bare wood but big time after finish is applied. It reminds me of a childhood friend of mine who could not eat anything other than clear jello without creating a rings around the sun type look….food dirt. I saw that as it was occurring with varnishing and admittedly did nothing about it. One of the luxuries of making things for yourself.
No test shavings yet -the handle glue is drying as the plane sits here, and to some extent, so is a tung oil and wax sole. Just under 8 pounds – a nice weight for a fat guy like me if the upper end of possible use includes rosewood. And nice even in cherry, especially cherry of suspicious quality or grading.